Internet Addiction Statistics: Prevalence and Impact


Internet usage has become almost inseparable from everyday life, yet many users struggle to maintain healthy limits. Over the past decade, researchers have increasingly recognized internet addiction as a critical public health and social issue.
Most definitions describe internet addiction as excessive, compulsive online engagement that disrupts normal routines and functioning.
This article explores recent data on prevalence, demographic differences, associated health risks, and treatment outcomes. By examining these statistics, we gain insights into the scope of internet addiction and the importance of effective interventions.
- An estimated 14% of the global population meets the criteria for internet addiction, though rates vary across studies.
- In some countries, up to 20% of adolescents display problematic online behaviors.
- Smartphone overuse has risen to nearly 27% worldwide, reflecting the ubiquity of mobile devices.
- Internet addiction frequently coexists with other mental health disorders, including depression and anxiety.
Age Group Trends and Risk Factors
Understanding which age groups are most at risk helps guide targeted prevention efforts.
- Adolescents and young adults have the highest rates of internet addiction globally. In some regions, nearly half of teenagers surveyed show signs of problematic use.
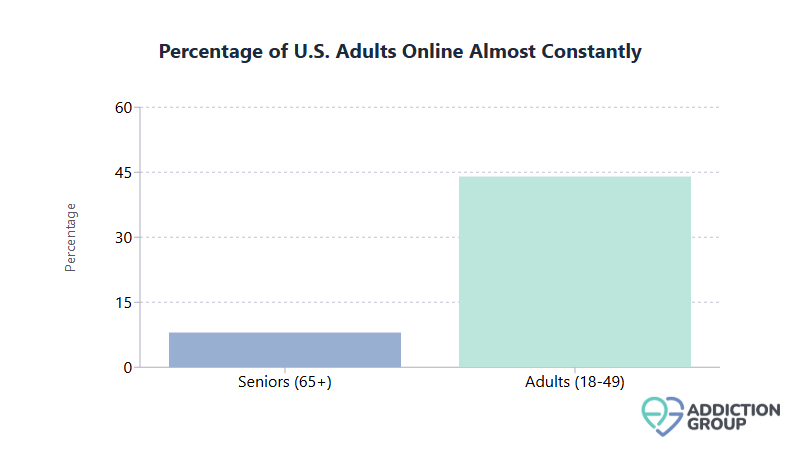
- Among U.S. seniors aged 65 and older, only about 8% report being online almost constantly, compared to nearly 44% of adults aged 18 to 49.
- Adolescent groups in East Asia often exhibit double-digit prevalence: in certain surveys, 19 to 24% of teens met diagnostic criteria for internet addiction.
- Younger individuals may be more susceptible due to digital immersion from an early age, social pressures, and the dominance of online entertainment in youth culture.
Device-Specific Usage Patterns
Different digital devices have varying impacts on addictive tendencies.
- Smartphones lead the way, with over 96% of internet users worldwide accessing the web by phone. Excessive phone-checking and social media scrolling fuel many addiction cases.
- Desktop and laptop computers remain significant, particularly for gaming and extended web browsing. Approximately 60% of users still go online via personal computers.
- Tablets, although widely owned, account for a smaller share of overall online time and thus represent a lower percentage of addiction cases.
Sleep Disruption and Physical Effects
Excessive screen time, especially late at night, can directly interfere with healthy sleep and physical well-being.
- Studies link internet addiction to poor sleep quality, insomnia, and daytime fatigue. Spending hours on social media or gaming before bed is a primary culprit.
- Heavy phone or computer usage can shift circadian rhythms, leading to difficulty falling asleep and frequent nighttime awakenings.
- Sedentary behavior from prolonged screen use contributes to weight gain, muscle stiffness, and other health complications such as chronic neck and back pain.
- Many internet-addicted individuals experience digital eye strain, with symptoms like headaches, dry eyes, and reduced visual acuity.
Academic and Workplace Consequences
When online activities overshadow responsibilities, it can erode performance in school or on the job.
- Research indicates that students with significant internet addiction often have lower grades and more incomplete assignments compared to their peers.
- Procrastination, fatigue, and distraction from frequent device checks hinder productivity, whether for study or employment.
- Overuse can also contribute to cognitive deficits, including reduced focus and memory, further undermining academic or occupational success.
Mental Health Comorbidity
Internet addiction frequently intersects with existing psychological conditions, making treatment more complex.
- Depression and anxiety are among the most common comorbidities. Individuals who are depressed may use the internet as a coping mechanism, while problematic use can exacerbate mood issues.
- ADHD symptoms correlate strongly with compulsive internet behaviors: in some studies, around half of adults with internet addiction screened positive for attention-deficit traits.
- Other concerns include social phobia and, in some cases, concurrent substance use. These overlapping conditions often necessitate integrated, multi-pronged treatment strategies.
Treatment Outcomes and Approaches
While no single solution works for everyone, several interventions show promise in addressing internet addiction.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) remains the most researched modality. Clinical trials report moderate-to-large reductions in addictive behaviors, sometimes moving users from “addicted” to “healthy” ranges.
- Structured “digital detox” camps in some Asian countries offer temporary device-free environments combined with counseling, skill-building, and monitored exercise. Many programs claim high short-term success rates.
- School-based interventions and short-term counseling for adolescents have reduced excessive screen habits and improved academic outcomes when followed consistently.
- The best results generally come from holistic programs that address online habits, underlying mental health issues, and familial or social dynamics.
Social and Familial Impact
Extended hours online often diminish real-life relationships and family cohesion.
- Many addicted users experience social isolation, forgoing in-person interaction in favor of digital pursuits. Over time, this can weaken friendships and romantic partnerships.
- Adolescents with problematic internet use frequently report higher loneliness scores, intensifying their reliance on online connections.
- Family conflicts arise from disputes over screen time, secrecy about usage, and neglected responsibilities. Warm, consistent parenting with firm boundaries appears protective against adolescent internet addiction.
Geographic Differences in Prevalence
Cultural norms and economic factors shape how internet addiction emerges around the world.
- East Asia reports some of the highest rates, with double-digit prevalence among adolescents in China, Taiwan, and South Korea.
- Middle Eastern regions also show elevated rates, with some local surveys reporting 30% or higher among specific youth populations.
- North America and Western Europe generally land in the lower single-digit percentages, though heavy daily screen use is still common.
- In some developing nations, a high proportion of the connected population exhibits problematic use, possibly driven by limited real-life opportunities and stressors.
Socioeconomic Considerations
Socioeconomic status intersects with internet addiction risk in multifaceted ways.
- On an international scale, lower-middle-income countries often report higher prevalence among those who do have reliable internet access.
- Economic hardships may spur individuals to escape into digital worlds, leading to higher rates of compulsive usage.
- Within wealthier nations, high-income groups have more device access but may also have greater resources for managing screen time, leaving rates of severe addiction relatively lower but not absent.
Screen Time Milestones
Overall, screen time has steadily climbed, fueled by social media, streaming, gaming, and mobile connectivity.
- The global average surpasses 6 hours of internet-based screen use per day. Certain regions, such as the Philippines, exceed 10 hours daily.
- Lockdowns during the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated this trend, coinciding with a notable uptick in reported digital addiction.
- U.S. surveys indicate that 31% of adults and roughly 45% of younger adults are online almost constantly, providing fertile ground for compulsive use patterns.
Activity-Specific Risks
Not all online pursuits carry the same probability of developing into an addictive habit.
- Social media and smartphone use top the charts, with around 17% and 27% of global users, respectively, showing signs of addiction in each category.
- Internet gaming disorder affects roughly 6% of the population, disproportionately young males.
- Cybersex addiction and online shopping also emerge as notable subtypes, though their overall rates are slightly lower.
Gender Differences
While overall prevalence may be similar between men and women, the nature of addictive use often diverges.
- Males are more prone to gaming or competitive platforms, leading to higher rates of gaming-specific addiction.
- Females tend to gravitate toward social media and smartphone-related overuse. Some research suggests women’s risk of social networking addiction outpaces that of men.
- Gender-informed prevention strategies, such as focusing on gaming triggers for boys and social media boundaries for girls, may boost intervention success.
Family Dynamics and Parenting Challenges
When children or teens become dependent on the digital realm, parents often struggle to manage conflicts and enforce limits.
- Household communication typically deteriorates as online activities replace face-to-face interactions.
- Conflict arises from repeated power struggles over device access, leading to friction and resentments within the family unit.
- Family-based therapy or counseling can significantly improve outcomes, emphasizing balanced tech use, better communication, and emotional support structures.
Effectiveness of Recovery Programs
Long-term healing from internet addiction typically involves ongoing intervention rather than a one-time fix.
- Multi-week digital detox can break cyclical behavior, but follow-up support remains crucial for relapse prevention.
- CBT-based interventions consistently show benefits, especially when addressing co-occurring conditions like depression or anxiety.
- Combining counseling, family therapy, and skill-building generally leads to deeper and more sustained reductions in compulsive internet use.
- The most successful programs help participants develop alternative hobbies, coping mechanisms, and a healthier relationship with technology overall.
In many parts of the world, internet addiction is rising in tandem with expanding digital infrastructure. The data shows that adolescents and young adults remain especially vulnerable, with increased risk in societies where device usage is socially ubiquitous or where offline opportunities are limited.
At the same time, addiction patterns are multifaceted: although some users compulsively game, others fall into social media spirals, binge streaming, or even online shopping disorders.
Interventions are gradually evolving to address not just the behavior itself but also its underlying drivers, whether they’re mental health challenges, family dynamics, or socioeconomic stressors.
Even as screens dominate more aspects of daily life, diverse strategies can redirect usage toward healthier patterns. Looking ahead, the hope is to harness technology as a beneficial resource without letting it overshadow the interpersonal connections and well-being that truly sustain human flourishing.
- Rumpf et al. “Occurence of Internet Addiction in a General Population Sample: A Latent Class Analysis.” Eur Addict Res, 2014.
- “Share of online users in the United States who report being addicted to social media as of April 2019, by age group.” Statista.
- Sserunkuuma et al. “Problematic use of the internet, smartphones, and social media among medical students and relationship with depression: An exploratory study.” PLOS ONE, 2023.
- Duong XL, Liaw SY, Augustin JPM. “How has Internet Addiction been Tracked Over the Last Decade? A Literature Review and 3C Paradigm for Future Research.” Int J Prev Med, 2020.
- “Share of online users in the United States who report being addicted to social media as of April 2019, by gender.” Statista.
- Walton AG. “Phone Addiction Is Real -- And So Are Its Mental Health Risks.” Forbes.com, 2022.
- “How Do Smartphones Affect Mental Health?” Therapy Brands.


