Gaming Addiction: National Trends and Statistics


Gaming addiction, sometimes referred to as “gaming disorder,” has rapidly emerged as a serious public health concern.
Although playing video games is a mainstream pastime for millions of Americans, a subset of individuals experience compulsive, harmful gaming patterns.
Over the last decade, researchers have increasingly focused on identifying how prevalent gaming addiction is, who is most affected, and what broader social and economic impacts arise.
In this article, we will explore national trends and key demographics, highlight significant findings on health and financial outcomes, and discuss both treatment and prevention strategies.
- Nearly 90% of U.S. teens report playing video games regularly, with up to 8% meeting clinical criteria for gaming addiction.
- Among young adults (ages 18 to 25), problematic gaming rose by 35% over the past ten years.
- Three to four times as many males as females report symptoms of gaming addiction, a gap commonly attributed to game genre preferences.
- In some treatment studies, over 60% of participants significantly reduced gaming time and related harms through structured therapy.
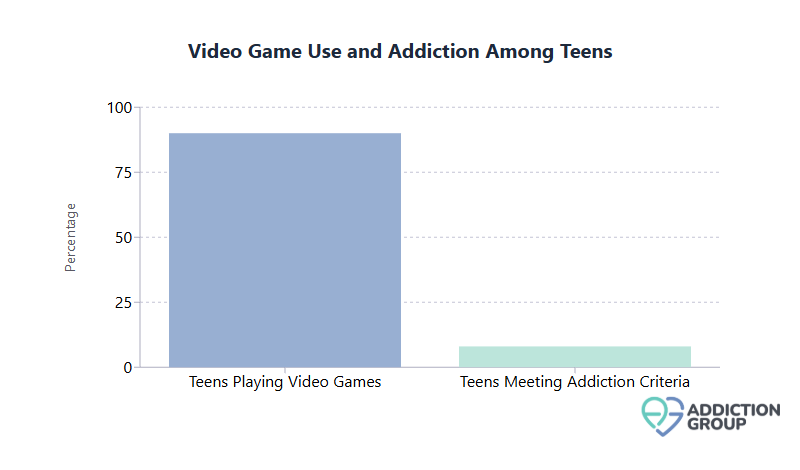
Understanding Why These Data Matter
Examining gaming addiction statistics provides insight into how modern lifestyles and digital entertainment intersect.
Recognizing which populations are most at risk and how excessive gaming affects physical, mental, and social health is crucial for developing effective intervention and prevention programs.
The data also illuminate the economic implications of gaming addiction, from healthcare costs to lost productivity.
Age-Stratified Prevalence
Age is one of the strongest predictors of gaming behavior and addiction risk. Younger players tend to devote more hours to gaming and, therefore, have higher odds of developing problematic patterns.
- Adolescents (12 to 17): Surveys from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) suggest that ~8% of adolescents who game exhibit compulsive or harmful behaviors, including missing school or neglecting assignments.
- College-Age Adults (18 to 25): Data from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) highlight a 35% increase in reported gaming addiction symptoms among this group over the last decade, partly attributed to more competitive online titles and campus social pressures.
- Adults (26 and older): While gaming is widespread in older groups, the overall addiction rate appears lower. However, many adults who do develop problematic gaming patterns report significant work and family disruptions.
Why It Matters
Interventions often focus on youth prevention, but data show that college students and even working professionals can struggle with uncontrolled gaming. Each age group benefits from tailored outreach.
Game Genres and Modes of Play
Not all games carry the same addiction risk. Certain genres use reward loops, social competition, and ongoing progression systems that can amplify compulsive behaviors.
- Massively Multiplayer Online (MMO) Titles: MMO and MMORPG (Massively Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Game) players sometimes invest 20+ hours each week, driven by leveling systems and virtual communities.
- First-Person Shooters (FPS): Fast-paced, online FPS games can encourage continuous “just one more match” sessions, with some addicted gamers logging hundreds of hours per month.
- Mobile vs. Console/PC: Mobile gaming can be habit-forming due to microtransactions and quick play sessions. Yet studies show console/PC gamers have a higher rate of severe addiction, often due to more immersive titles.
- Multi-Platform Usage: Those who play across console, PC, and mobile devices face increased risk as games remain accessible throughout the day and night.
Why It Matters
By identifying which genres are most problematic, educators, clinicians, and parents can watch for red flags, such as extended play times, large in-game purchases, and clear difficulty stopping despite negative consequences.
Excessive Gaming Hours and Lifestyle Disruption
One hallmark of gaming addiction is the sheer number of hours spent playing. While the average gamer in the U.S. may play 6 to 8 hours per week, addicted individuals often double or triple that figure.
- Academic and Work Impact: Excessive gaming frequently leads to truancy, late or incomplete work, and lower productivity on the job. In some cases, students’ GPAs have dropped below a passing threshold when compulsive gaming escalates.
- Social Isolation: Spending upwards of 20 hours per week in virtual worlds can replace real-world relationships and social experiences, sometimes causing conflict at home or withdrawal from extracurricular activities.
- Sleep Deprivation: Gaming late into the night or even through early morning hours disrupts normal sleep cycles. About 1 in 5 gamers admit to sacrificing sleep “often” to keep playing, with addicted gamers more likely to do so regularly.
Why It Matters
Excessive gameplay is a red flag for broader health issues. It hinders academic performance, strains relationships, and, over time, can compound stress or mental health challenges.
Physical and Mental Health Consequences
Though not a substance-based disorder, gaming addiction shares many symptoms with other behavioral addictions and often appears alongside mental health conditions.
- Anxiety and Depression: Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) highlight that adolescents with addictive gaming patterns are twice as likely to report frequent depressive episodes or heightened anxiety.
- Sedentary Lifestyles: Heavy gamers spend prolonged periods sitting, risking weight gain, posture problems, and lack of adequate exercise. Some specialists report a rise in musculoskeletal issues among patients who game excessively.
- Sleep Deficits: Chronic late-night gaming routines correlate with less than 5 to 6 hours of sleep, leading to fatigue, concentration problems, and greater irritability.
- ADHD and Impulse Control: The impulsivity linked to Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder can intensify compulsive gaming behaviors, creating a cycle of brief dopamine rewards that are difficult to resist.
Why It Matters
Pinpointing comorbidities helps healthcare providers develop comprehensive treatment plans. Addressing both the addictive gaming behavior and any underlying conditions (e.g., depression, anxiety) increases long-term recovery potential.
Financial Strain and In-Game Spending
A more subtle but crucial dimension of gaming addiction is the financial cost. Many modern games use microtransactions or “loot boxes” that invite frequent spending.
- Loot Box Purchases: Research accessed via the PubMed Database indicates that problem gamers are significantly more prone to buy randomized “loot boxes,” mirroring gambling-like behaviors.
- Spending Habits: In free-to-play (F2P) titles, a small percentage of “whale” spenders (many with addictive tendencies) can account for over 50% of a game’s revenue.
- Credit Card Debt: Stories of teens racking up thousands of dollars of charges have become more common, illustrating how addiction can extend beyond just time lost.
Why It Matters
Families and individuals who observe unexplained charges or hidden gaming purchases may catch early warning signs of addiction. Financial awareness and budgeting can be protective against escalating gaming expenses.
Family and Community Impact
Gaming addiction rarely exists in a vacuum; its ripple effects can influence entire households and communities.
- Strained Family Relationships: Parents frequently report conflicts over limits, with some households experiencing daily arguments about gaming time. Siblings might resent the addicted individual’s lack of participation in family duties.
- Romantic Tensions: Surveys show around 5% of gamers have experienced a lost or significantly damaged romantic relationship due to excessive gaming.
- Community Awareness: Some school districts are beginning to address gaming behaviors during health classes or in after-school programs, recognizing the need for early interventions.
Why It Matters
Family and community dynamics can either worsen or help resolve gaming addiction. Effective solutions typically involve a supportive, informed network rather than isolated changes by the gamer alone.
Treatment Approaches and Efficacy
As gaming addiction gains recognition, both inpatient and outpatient therapies have expanded in response. Treatment success hinges on addressing the psychological drivers behind compulsive gaming.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Research supported by the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services (HHS) indicates CBT tailored to behavioral addictions can yield over 60% reduction in problematic gaming hours and related distress.
- Motivational Interviewing (MI): Clinicians guide patients to recognize the dissonance between goals (e.g., academic or career aspirations) and current gaming habits, empowering self-directed change.
- Support Groups and Online Forums: Peer-driven platforms, including those modeled after 12-step programs, offer community support. Many participants find regular check-ins crucial for long-term relapse prevention.
Why It Matters
Treatment often restores balance in individuals’ lives, allowing them to reclaim goals and relationships. Early intervention, whether through counseling, peer support, or digital well-being apps, can prevent years of detrimental patterns.
Prevention Strategies and Early Education
Increasingly, schools and youth organizations are introducing “digital literacy” and “screen-time balance” lessons to preempt gaming addiction.
- School-Based Workshops: Some interventions reported via the National Survey on Drug Use and Health show that students who learn self-regulation and time-management strategies are 30 to 40% less likely to escalate into problem gaming.
- Parental Controls and Supervision: Built-in time limit tools, content filters, and open discussions about gaming can reduce risk factors for adolescents.
- Community Outreach: Local health departments, libraries, and community centers sometimes offer seminars for parents on managing screen time and spotting addiction warning signs.
Why It Matters
Prevention, especially during critical developmental windows, mitigates future health and social burdens. Investing resources in education can spare families from more intensive interventions later on.
A Snapshot of Key Indicators (Table)
Below is a simple table highlighting selected findings from national data and research surveys:
| Indicator | Approximate Figure | Source/Notes |
| Adolescent Addiction Rate | 8% of regular teen gamers | NSDUH |
| Highest-Risk Age Range | 18–25 years old | NIDA |
| Male-to-Female Ratio | ~3:1 (addiction prevalence) | CDC, various school-based studies |
| Weekly Hours (Addicted Gamers) | 20+ hours (often double typical gamers’ time) | HHS |
| Primary Treatment Success (CBT) | 60%+ reduction in problematic behaviors | PubMed Database |
Final Thoughts
Gaming addiction in the United States reflects a broader trend of digital behaviors intersecting with mental and physical health. The core concern is not gaming per se, as many enjoy it as a healthy pastime, but the transition from casual play to a compulsive habit that displaces essential life activities.
Statistics consistently pinpoint youth and young adults as the most vulnerable groups, highlighting the importance of monitoring time spent on competitive or immersive games.
Effective treatments, especially cognitive behavioral interventions, demonstrate promising success rates. Comprehensive approaches often include therapy, community support, and strategies to manage co-occurring conditions such as anxiety or ADHD.
In the bigger picture, gaming addiction data underscore the need for nuanced public health policies and resources. From health insurance coverage for behavioral addictions to in-school modules that foster responsible screen habits, society is learning how to address this modern challenge.
With continued research and awareness, we can balance the benefits of interactive media with effective safeguards against excessive use. Overcoming any addiction takes time, but the growing availability of specialized support offers hope to individuals and families.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – https://www.cdc.gov/data-statistics
- National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) – https://nida.nih.gov/research-topics/college-age-young-adults
- National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH), SAMHSA – https://www.samhsa.gov/data/report/2022-nsduh-annual-national-report
- PubMed Database – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17156173/
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services (HHS) – https://www.hhs.gov/opioids/


